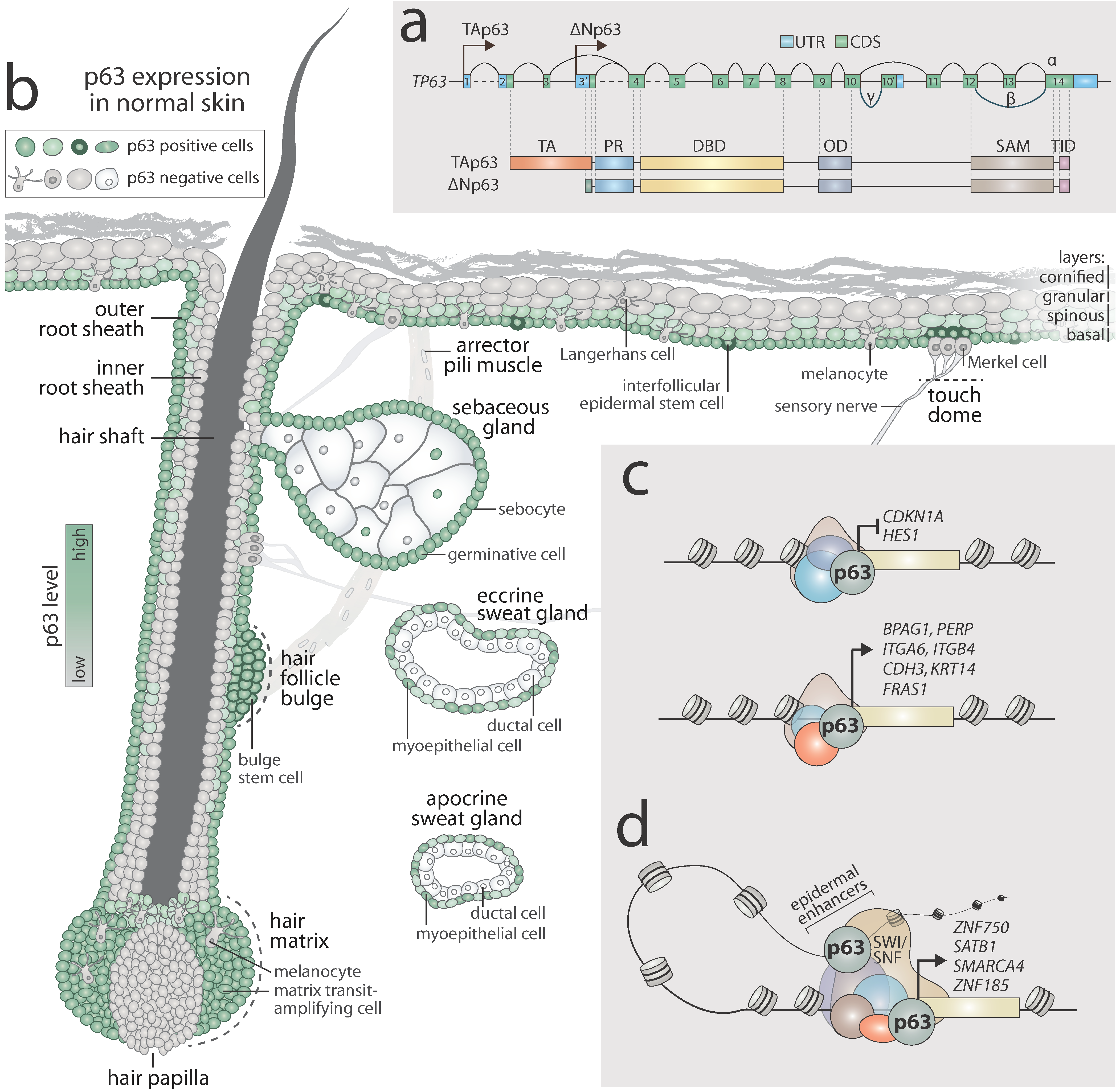
Immunohistochemical staining of p63 in various tissue samples. A-p63 in... | Download Scientific Diagram
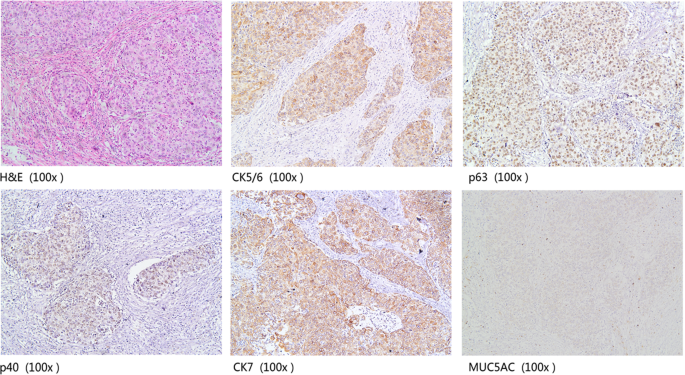
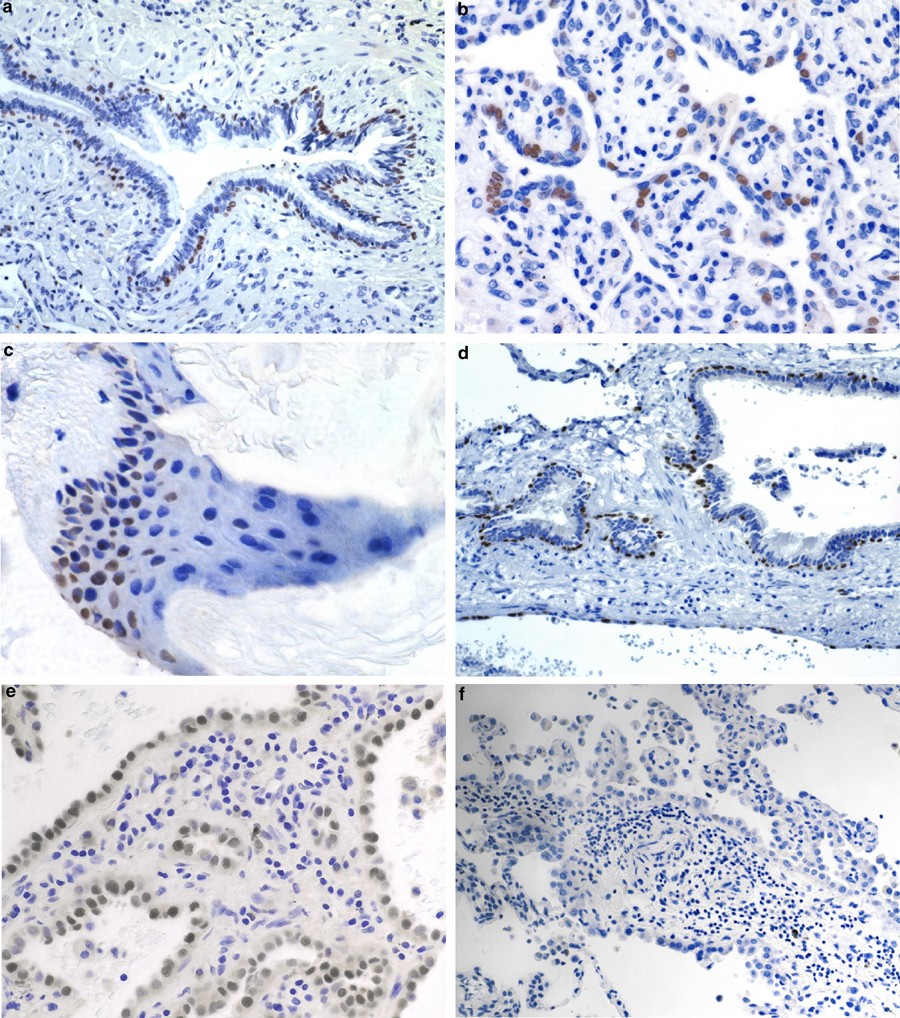
The Use of P63 Immunohistochemistry for the Identification of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung | PLOS ONE
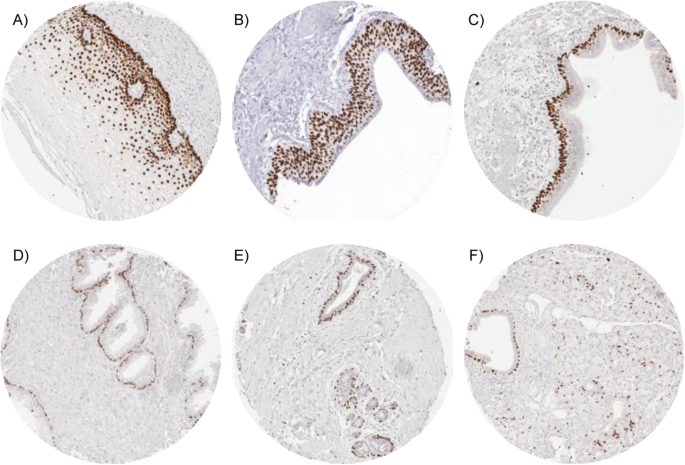
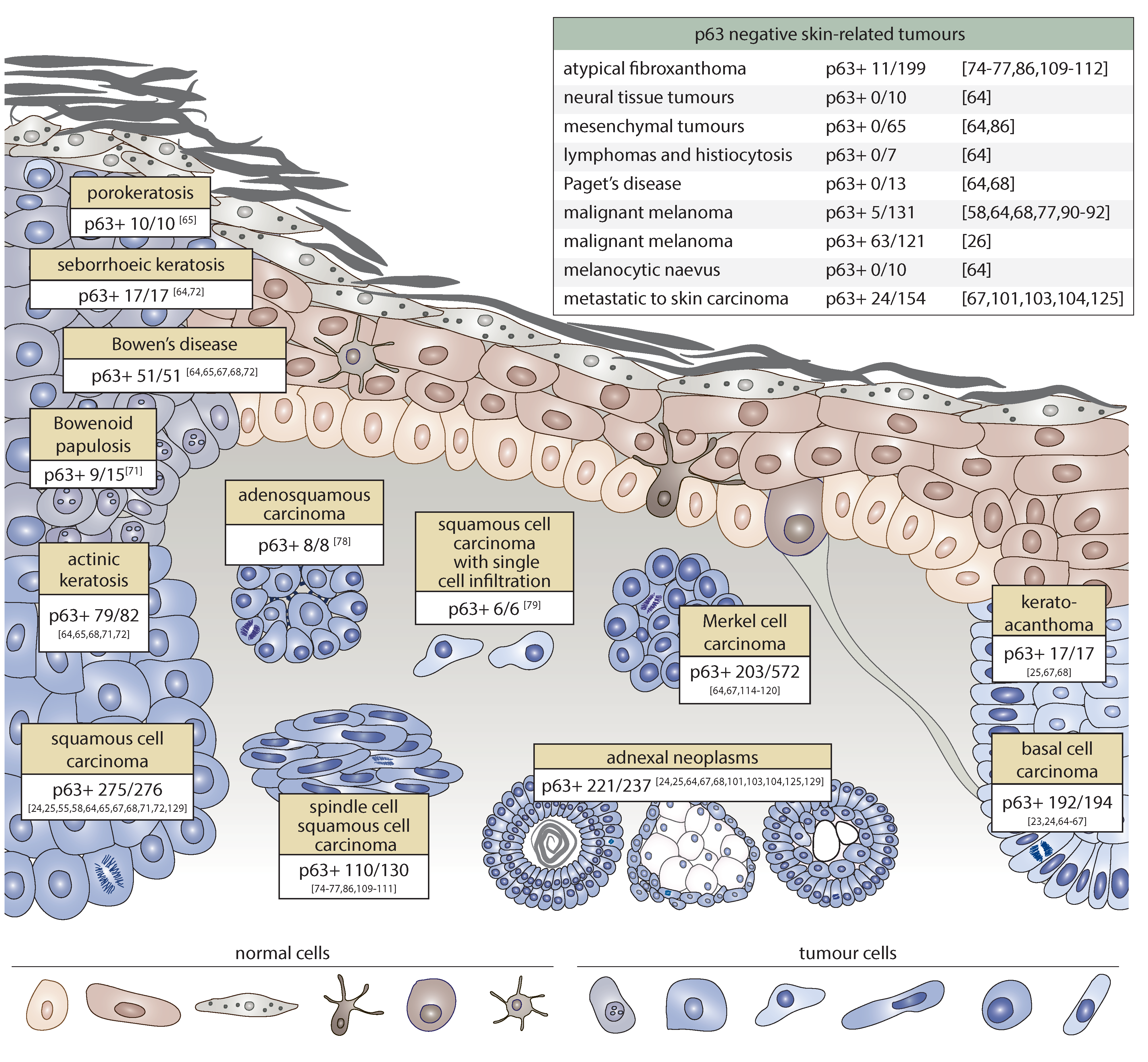
p63 expression in human tumors and normal tissues: a tissue microarray study on 10,200 tumors | Biomarker Research | Full Text

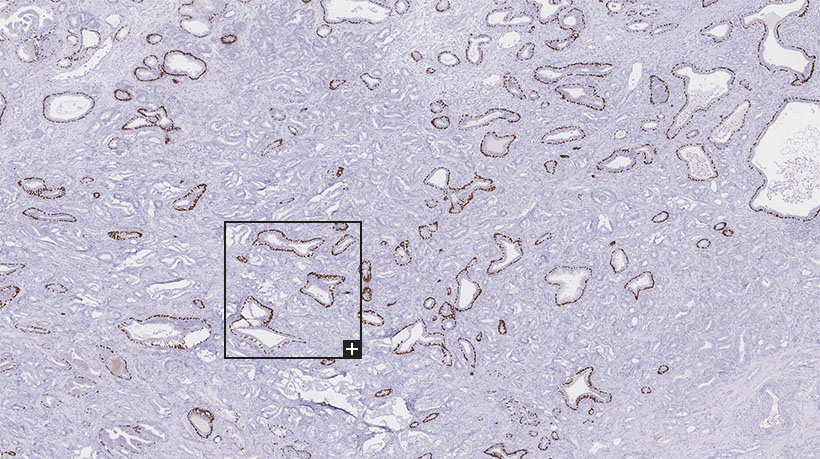
p63 expression in cancerous tissues. Strong p63 immunostaining is seen... | Download Scientific Diagram
The Use of P63 Immunohistochemistry for the Identification of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung | PLOS ONE
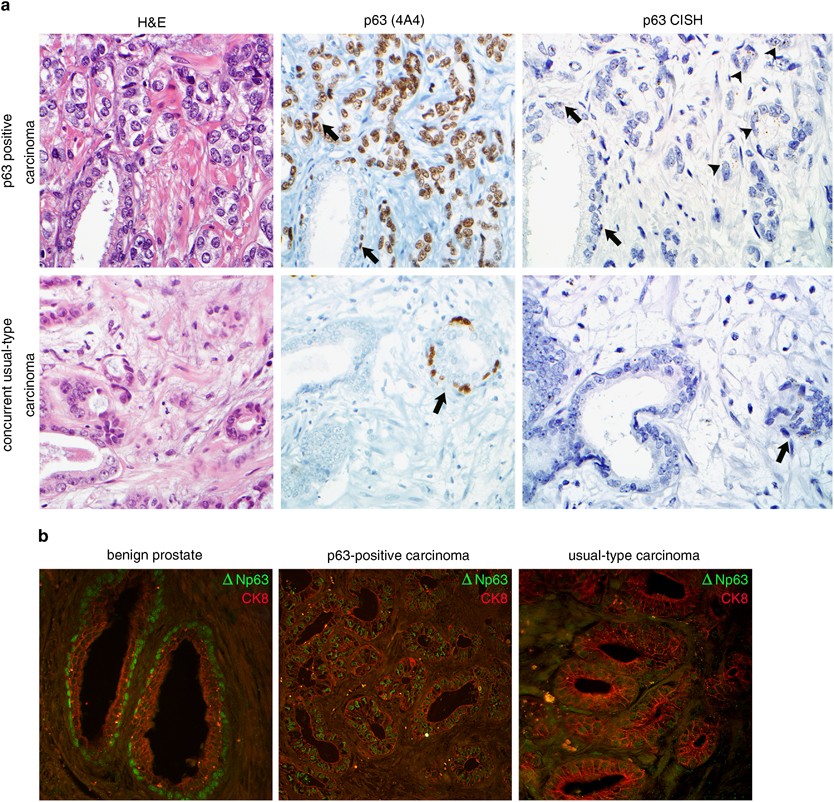
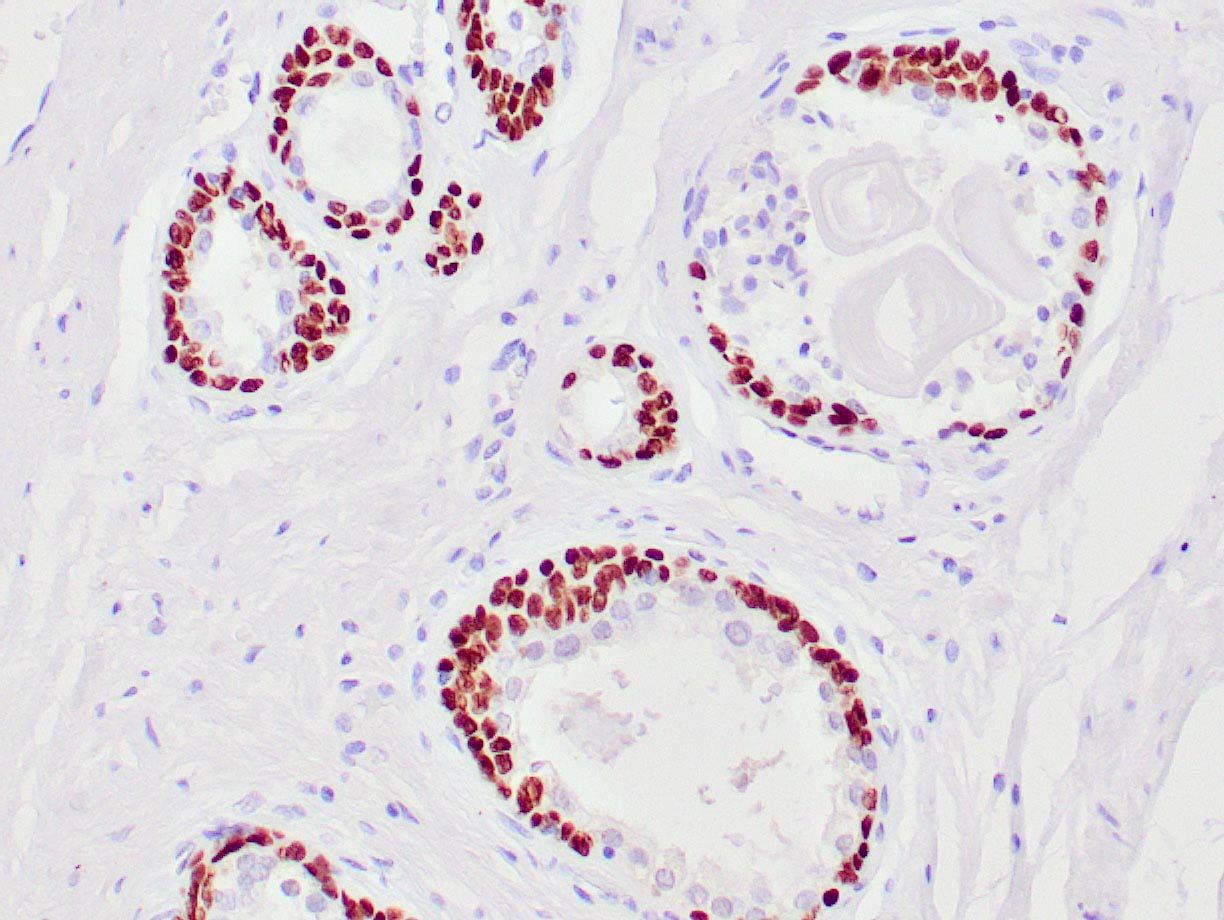
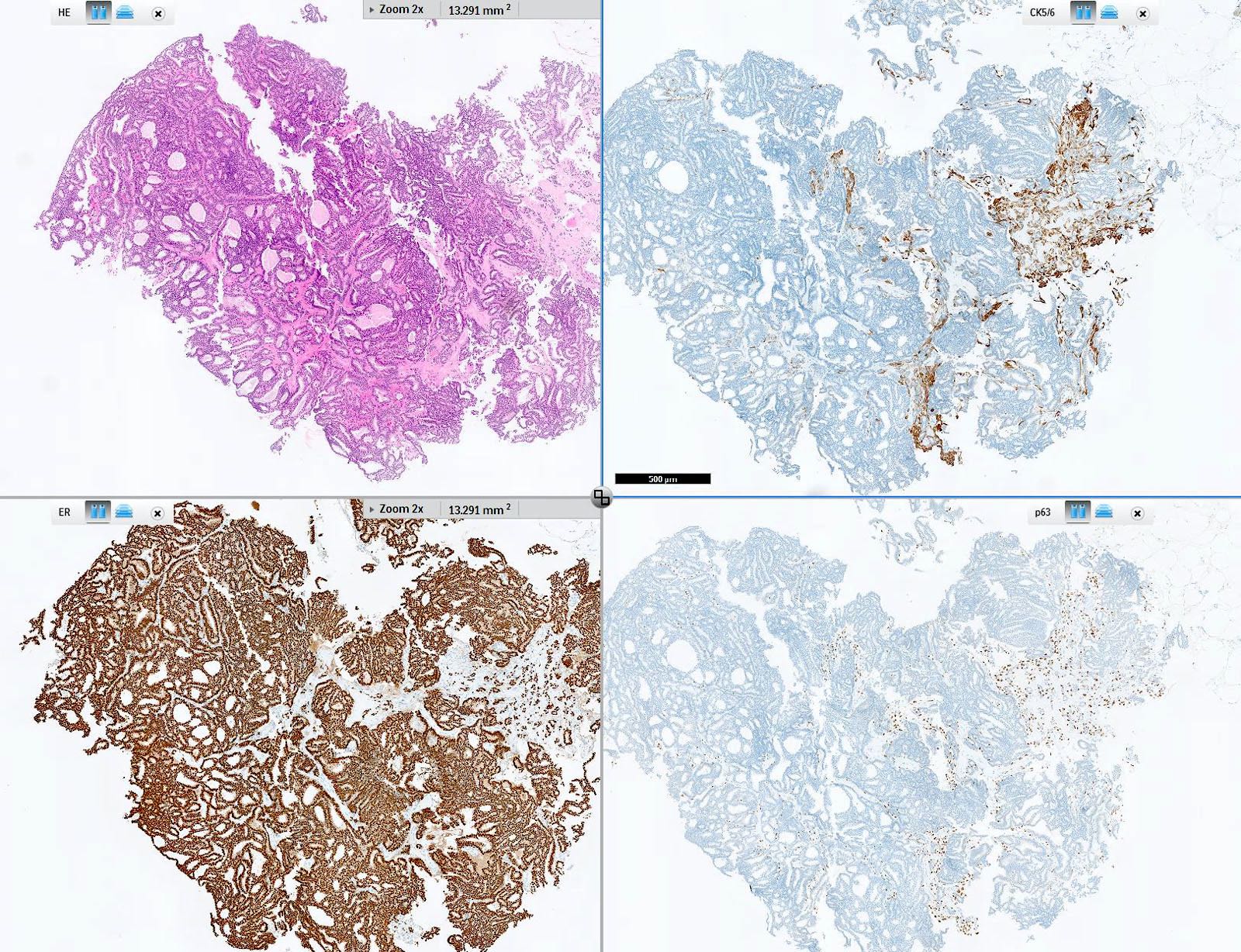
Prostate adenocarcinomas aberrantly expressing p63 are molecularly distinct from usual-type prostatic adenocarcinomas | Modern Pathology

Predictive markers for pathological complete response after neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer - ScienceDirect

p63 and SOX2 Dictate Glucose Reliance and Metabolic Vulnerabilities in Squamous Cell Carcinomas - ScienceDirect